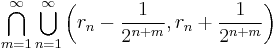Baire space
In mathematics, a Baire space is a topological space which, intuitively speaking, is very large and has "enough" points for certain limit processes. It is named in honor of René-Louis Baire who introduced the concept.
Contents |
Motivation
In an arbitrary topological space, the class of closed sets with empty interior consists precisely of the boundaries of dense open sets. These sets are, in a certain sense, "negligible". Some examples are finite sets, smooth curves in the plane, and proper affine subspaces in a Euclidean space. A topological space is a Baire space if it is "large", meaning that it is not a countable union of negligible subsets. For example, the three dimensional Euclidean space is not a countable union of its affine planes.
Definition
The precise definition of a Baire space has undergone slight changes throughout history, mostly due to prevailing needs and viewpoints. First, we give the usual modern definition, and then we give a historical definition which is closer to the definition originally given by Baire.
Modern definition
A topological space is called a Baire space if the union of any countable collection of closed sets with empty interior has empty interior.
This definition is equivalent to each of the following conditions:
- Every intersection of countably many dense open sets is dense.
- The interior of every union of countably many closed nowhere dense sets is empty.
- Whenever the union of countably many closed subsets of X has an interior point, then one of the closed subsets must have an interior point.
Historical definition
In his original definition, Baire defined a notion of category (unrelated to category theory) as follows.
A subset of a topological space X is called
- nowhere dense in X if the interior of its closure is empty
- of first category or meagre in X if it is a union of countably many nowhere dense subsets
- of second category or nonmeagre in X if it is not of first category in X
The definition for a Baire space can then be stated as follows: a topological space X is a Baire space if every non-empty open set is of second category in X. This definition is equivalent to the modern definition.
A subset A of X is comeagre if its complement 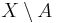 is meagre. A topological space X is a Baire space if and only if every comeager subset of X is dense.
is meagre. A topological space X is a Baire space if and only if every comeager subset of X is dense.
Examples
- The space R of real numbers with the usual topology, is a Baire space, and so is of second category in itself. The rational numbers are of first category and the irrational numbers are of second category in R.
- The Cantor set is a Baire space, and so is of second category in itself, but it is of first category in the interval [0, 1] with the usual topology.
- Here is an example of a set of second category in R with Lebesgue measure 0.
- where
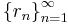 is a sequence that enumerates the rational numbers.
is a sequence that enumerates the rational numbers.
- Note that the space of rational numbers with the usual topology inherited from the reals is not a Baire space, since it is the union of countably many closed sets without interior, the singletons.
Baire category theorem
The Baire category theorem gives sufficient conditions for a topological space to be a Baire space. It is an important tool in topology and functional analysis.
- (BCT1) Every complete metric space is a Baire space. More generally, every topological space which is homeomorphic to an open subset of a complete pseudometric space is a Baire space. In particular, every topologically complete space is a Baire space.
- (BCT2) Every locally compact Hausdorff space is a Baire space.
BCT1 shows that each of the following is a Baire space:
- The space R of real numbers
- The space of irrational numbers
- The Cantor set
- Indeed, every Polish space
BCT2 shows that every manifold is a Baire space, even if it is not paracompact, and hence not metrizable. For example, the long line is of second category.
Properties
- Every non-empty Baire space is of second category in itself, and every intersection of countably many dense open subsets of X is non-empty, but the converse of neither of these is true, as is shown by the topological disjoint sum of the rationals and the unit interval [0, 1].
- Every open subspace of a Baire space is a Baire space.
- Given a family of continuous functions fn:X→Y with pointwise limit f:X→Y. If X is a Baire space then the points where f is not continuous is a meagre set in X and the set of points where f is continuous is dense in X. A special case of this is the uniform boundedness principle.
See also
References
- Munkres, James, Topology, 2nd edition, Prentice Hall, 2000.
- Baire, René-Louis (1899), Sur les fonctions de variables réelles, Annali di Mat. Ser. 3 3, 1--123.